Step 1– Create A Unit File
Open a sample unit file using the command as shown below:
sudo nano /lib/systemd/system/sample.service
Add in the following text :
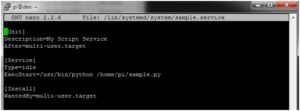
[Unit] Description=My Sample Service After=multi-user.target [Service] Type=idle ExecStart=/usr/bin/python /home/pi/sample.py [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
You should save and exit the nano editor.
This defines a new service called “Sample Service” and we are requesting that it is launched once the multi-user environment is available. The “ExecStart” parameter is used to specify the command we want to run. The “Type” is set to “idle” to ensure that the ExecStart command is run only when everything else has loaded. Note that the paths are absolute and define the complete location of Python as well as the location of our Python script.
In order to store the script’s text output in a log file you can change the ExecStart line to:
ExecStart=/usr/bin/python /home/pi/sample.py > /home/pi/sample.log 2>&1
The permission on the unit file needs to be set to 644 :
sudo chmod 644 /lib/systemd/system/sample.service
Step 2 – Configure systemd
Now the unit file has been defined we can tell systemd to start it during the boot sequence :
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl enable sample.service
Reboot the Pi and your custom service should run:
sudo reboot
Creating GUI applications for raspberry pi using cross compilation is a process that includes multiple stages, Like Executable Binary creation on Host Machine, transferring executable on target, and executing binary on target.
mkdir ~/app && cd ~/app
scp remoteHostname@RemoteIP:/appLocationOnRemote/my_app
Launch Script
sudo nano launch_MyApp.sh
#!/bin/sh
sudo /home/pi/app/my_app
sudo chmod +x launch_MyApp.sh
Calling Launch Script on startup
sudo nano ~/.config/autostart/MyApp.desktop
Desktop Entry]
Type=Application
Name=My_App
Exec=/bin/bash /home/pi/app/launch_MyApp.sh
Kill Script
sudo nano kill_MyApp.sh
#!/bin/sh
if pgrep -x "my_app" > /dev/null
then
pgrep -x "my_app" | sudo xargs kill
fi
sudo chmod +x kill_MyApp.sh
Synchronize and run binary
sudo nano ~/.bashrc
export XAUTHORITY=~/.Xauthority
export DISPLAY=:0;
sudo nano sync_MyApp.sh
sudo chmod +x sync_MyApp.sh
#!/bin/sh
if pgrep -x "my_app" > /dev/null
then
pgrep -x "my_app" | sudo xargs kill
fi
scp remoteHostname@RemoteIP:/appLocationOnRemote/my_app
/home/pi/app/my_app